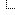10-07-2014, 02:57 PM
Ex-Facebook Data Scientist: Every Facebook User Is Part Of An Experiment At Some Point
Andrew Ledvina used to be a data scientist at Facebook. He recently made the mistake of talking to a reporter about that, notably telling a WSJ reporter that when he was there from 2012 to 2014, there was no internal review board that might have had qualms about Facebook's now infamous emotion manipulation study, that he and other data scientists were allowed to run any test they wanted as long as it didn't annoy users, and that people working there get "desensitized" to the number of people included in their experiments as it's such a tiny percentage of Facebook's overall user base. Ledvina, like many a person quoted in the media, didn't like the way the reporter presented his words and so took to his blog to defend himself, Facebook, and the Facebook study but I think he simply dug a deeper hole for the company that he quit this April. He facetiously titled the blog, "10 Ways Facebook Is Actually The Devil," to needle those who see the study as evil, and then went on to confirm the WSJ's report and shed new light on how Facebook's data science team views users.
1. The Facebook emotion manipulation study didn't get vetted before it was run on users, but it likely did get vetted by Facebook's PR and legal team before it went into a scholarly journal; they apparently didn't think it would make people angry and result in a reported investigation in Europe and legal complaint with the FTC in the States.
Ledvina: "While I was at Facebook, there was no institutional review board that scrutinized the decision to run an experiment for internal purposes. Once someone had a result that they decided they wanted to submit for publication to a journal, there definitely was a back and forth with PR and legal over what could be published."
2. If you're on Facebook, you have definitely been a test subject at some point.
Ledvina: "Experiments are run on every user at some point in their tenure on the site…"
3. But you may have been a test subject in a very boring experiment.
Ledvina: "…Whether that is seeing different size ad copy, or different marketing messages, or different call to action buttons, or having their feeds generated by different ranking algorithms, etc." [Ed Note: Link on "call to action" is mine not Ledvina's.]
4. This ex-employee of Facebook still doesn't understand why people are upset that Facebook researchers tried to see if they could upset people.
Ledvina: "The fundamental purpose of most people at Facebook working on data is to influence and alter people's moods and behaviour. They are doing it all the time to make you like stories more, to click on more ads, to spend more time on the site. This is just how a website works, everyone does this and everyone knows that everyone does this, I don't see why people are all up in arms over this thing all of a sudden."
5. Facebook researchers forget that what they're doing has an effect on the real live people that use Facebook.
Ledvina: "Every data scientist at Facebook that I have ever interacted with has been deeply passionate about making the lives of people using Facebook better, but with the pragmatic understanding that sometimes you need to hurt the experience for a small number of users to help make things better for 1+ billion others. That being said, all of this hubbub over 700k users like it is a large number of people is a bit strange coming from the inside where that is a very tiny fraction of the user base (less than 0.1%), and even that number is likely inflated to include a control group. It truly is easy to get desensitized to the fact that those are nearly 1M real people interacting with the site."
Ledvina expressed surprise that the experiment playing with the emotional content of users' News Feeds was getting so much play in the press while other Facebook research has been ignored. He pointed to an event last year, where Facebook researchers and academic researchers got together to talk about work done to see how "Facebook and social networks in general can be more compassionate," and prevent bullying particularly among teens. "I am a bit taken aback by the fact that the most recent paper has gotten as much press as it has, when the work done as part of the compassion research days has never been mentioned," he writes. "Some of these papers are based on experiments that influence people's behavior in similar ways, but I guess they do not have as much cachet for whatever reason."
I went ahead and watched the hours of presentations archived by Facebook from the "Compassion Research Day." There were a couple of key differences from the January 2012 manipulation study. First, none of the work done by the researchers aimed to make people feel worse. Secondly, the research on people's behavior was far less surreptitious. Thirdly, researchers didn't interfere with people's "natural" experience of the site beyond obvious (and some not-so obvious) prompts for feedback.
One of the videos about "new tools to understand people" doesn't have a presenter talking about trying to influence people's emotional state in a negative way and then measure it by monitoring their status updates. " We asked users, What are you trying to do? Why did you click that button?'" says the presenter. "We learned a lot from asking people for feedback."
This is a transparent way of "running tests" on users, presenting them with questions and asking them for feedback, a rather traditional approach to experimentation. Another presenter talked about measuring emotion by asking people to put "emoticon" faces on their status updates. Okay, Facebook users may not have realized they got these cute digital stickers for Facebook to measure their emotional states, but it's at least a translucent way of taking users' emotional temperature.
In trying to see how teens deal with stuff they don't like on the site, Facebook proactively asked the youngish ones how they felt when they flagged something they didn't like. That's a far more aboveboard approach than the one taken by the Facebook data scientist in the 2012 emotion study. The researchers were trying to find out why people get offended and how they resolve the issue, and giving them better tools to aid the process, which is all a far cry from turning the tone of News Feeds negative to see if it makes someone blue and turns them off using Facebook. The perhaps unexpected thing done by the compassion researchers' is collecting the messages Facebook users send to other users when asking them to take down an embarrassing photo or offensive post; they do this to try to understand why people object to content on the site.
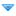
![[Image: Facebook-asking-people-how-they-feel.jpg]](http://blogs-images.forbes.com/kashmirhill/files/2014/07/Facebook-asking-people-how-they-feel.jpg) Facebook asking users how a post made them feel, rather than secretly divining it from their status updates
Facebook asking users how a post made them feel, rather than secretly divining it from their status updates![[Image: Facebook-asking-for-feedback.jpg]](http://blogs-images.forbes.com/kashmirhill/files/2014/07/Facebook-asking-for-feedback.jpg) Facebook's innovation' in gauging feedback, as presented at a company event in December 2013
Facebook's innovation' in gauging feedback, as presented at a company event in December 2013Ledvina is pessimistic about the hubbub' over the study leading to any change at Facebook, though he makes very clear that he is an ex-employee who knows little about the inner workings at Facebook now. "The only thing I see changing from this is not whether similar experiments will be run, but rather [whether they will] be published," he writes, confirming the outcome that many commentators, including the New York Times' Farhad Manjoo, fear. "Similar experiments have been and will continue to be run, but you probably just won't see a paper about it anymore."
http://www.forbes.com/sites/kashmirhill/...ome-point/
"The philosophers have only interpreted the world, in various ways. The point, however, is to change it." Karl Marx
"He would, wouldn't he?" Mandy Rice-Davies. When asked in court whether she knew that Lord Astor had denied having sex with her.
“I think it would be a good idea” Ghandi, when asked about Western Civilisation.
"He would, wouldn't he?" Mandy Rice-Davies. When asked in court whether she knew that Lord Astor had denied having sex with her.
“I think it would be a good idea” Ghandi, when asked about Western Civilisation.