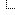Posts: 16,285
Threads: 1,789
Likes Received: 7 in 7 posts
Likes Given: 0
Joined: Sep 2008
Pete Seeger, Songwriter and Champion of Folk Music, Dies at 94By JON PARELESJAN. 28, 2014
![[Image: 28seeger1-master675.jpg]](http://static01.nyt.com/images/2014/01/28/arts/music/28seeger1/28seeger1-master675.jpg) Launch media viewer Launch media viewer
Pete Seeger at the Beacon Sloop Club in Beacon, N.Y., in 2010.
Pete Seeger, the singer, folk-song collector and songwriter who spearheaded an American folk revival and spent a long career championing folk music as both a vital heritage and a catalyst for social change, died Monday. He was 94 and lived in Beacon, N.Y.
His death was confirmed by his grandson, Kitama Cahill Jackson, who said he died of natural causes at NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital.
Mr. Seeger's career carried him from singing at labor rallies to the Top 10 to college auditoriums to folk festivals, and from a conviction for contempt of Congress (after defying the House Un-American Activities Committee in the 1950s) to performing on the steps of the Lincoln Memorial at an inaugural concert for Barack Obama.
For Mr. Seeger, folk music and a sense of community were inseparable, and where he saw a community, he saw the possibility of political action.
In his hearty tenor, Mr. Seeger, a beanpole of a man who most often played 12-string guitar or five-string banjo, sang topical songs and children's songs, humorous tunes and earnest anthems, always encouraging listeners to join in. His agenda paralleled the concerns of the American left: He sang for the labor movement in the 1940s and 1950s, for civil rights marches and anti-Vietnam War rallies in the 1960s, and for environmental and antiwar causes in the 1970s and beyond. "We Shall Overcome," which Mr. Seeger adapted from old spirituals, became a civil rights anthem.
Mr. Seeger was a prime mover in the folk revival that transformed popular music in the 1950s. As a member of the Weavers, he sang hits including Lead Belly's"Goodnight, Irene" which reached No. 1 and "If I Had a Hammer," which he wrote with the group's Lee Hays. Another of Mr. Seeger's songs, "Where Have All the Flowers Gone?," became an antiwar standard. And in 1965, the Byrds had a No. 1 hit with a folk-rock version of "Turn! Turn! Turn!," Mr. Seeger's setting of a passage from the Book of Ecclesiastes.
Mr. Seeger was a mentor to younger folk and topical singers in the 50s and 60s, among them Bob Dylan, Don McLean and Bernice Johnson Reagon, who founded Sweet Honey in the Rock. Decades later, Bruce Springsteen drew the songs on his 2006 album, "We Shall Overcome: The Seeger Sessions," from Mr. Seeger's repertoire of traditional music about a turbulent American experience, and in 2009 he performed Woody Guthrie's "This Land Is Your Land" with Mr. Seeger at the Obama inaugural. At a Madison Square Garden concert celebrating Mr. Seeger's 90th birthday, Mr. Springsteen introduced him as "a living archive of America's music and conscience, a testament of the power of song and culture to nudge history along."
Although he recorded more than 100 albums, Mr. Seeger distrusted commercialism and was never comfortable with the idea of stardom. He invariably tried to use his celebrity to bring attention and contributions to the causes that moved him, or to the traditional songs he wanted to preserve.
Mr. Seeger saw himself as part of a continuing folk tradition, constantly recycling and revising music that had been honed by time.
During the McCarthy era Mr. Seeger's political affiliations, including membership in the Communist Party in the 1940s, led to his being blacklisted and later indicted for contempt of Congress. The pressure broke up the Weavers, and Mr. Seeger disappeared from television until the late 1960s. But he never stopped recording, performing and listening to songs from ordinary people. Through the decades, his songs have become part of America's folklore.
"My job," he said in 2009, "is to show folks there's a lot of good music in this world, and if used right it may help to save the planet."
Peter Seeger was born on May 3, 1919, to Charles Seeger, a musicologist, and Constance de Clyver Edson Seeger, a concert violinist. His parents later divorced.
He began playing the ukulele while attending Avon Old Farms, a private boarding school in Connecticut. His father and his stepmother, the composer Ruth Crawford Seeger, were collecting and transcribing rural American folk music, as were folklorists like John and Alan Lomax. He heard the five-string banjo, which would become his main instrument, when his father took him to a square-dance festival in North Carolina.
Young Pete became enthralled by rural traditions. "I liked the strident vocal tone of the singers, the vigorous dancing," he is quoted in "How Can I Keep From Singing," a biography by David Dunaway. "The words of the songs had all the meat of life in them. Their humor had a bite, it was not trivial. Their tragedy was real, not sentimental."
Planning to be a journalist, Mr. Seeger attended Harvard, where he founded a radical newspaper and joined the Young Communist League. After two years, he dropped out and came to New York City, where Mr. Lomax introduced him to the blues singer Huddie Ledbetter, known as Lead Belly. Mr. Lomax also helped Mr. Seeger find a job cataloging and transcribing music at the Archive of American Folk Song at the Library of Congress.
Mr. Seeger met Mr. Guthrie, a songwriter who shared his love of vernacular music and agitprop ambitions, in 1940, when they performed at a benefit concert for migrant California workers. Traveling across the United States with Mr. Guthrie, Mr. Seeger picked up some of his style and repertory. He also hitchhiked and hopped freight trains by himself, trading and learning songs.
When he returned to New York later in 1940, Mr. Seeger made his first albums. He, Millard Lampell and Mr. Hays founded the Almanac Singers, who performed union songs and, until Germany invaded the Soviet Union, antiwar songs, following the Communist Party line. Mr. Guthrie soon joined the group.
During World War II the Almanac Singers's repertory turned to patriotic, antifascist songs, bringing them a broad audience, including a prime-time national radio spot. But the group's earlier antiwar songs, the target of an F.B.I. investigation, came to light, and the group's career plummeted.
Before the group completely dissolved, however, Mr. Seeger was drafted in 1942 and assigned to a unit of performers. He married Toshi-Aline Ohta while on furlough in 1943.
When he returned from the war he founded People's Songs Inc., which published political songs and presented concerts for several years before going bankrupt. He also started his nightclub career, performing at the Village Vanguard in Greenwich Village. Mr. Seeger and Paul Robeson toured with the campaign of Henry Wallace, the Progressive Party presidential candidate, in 1948.
Mr. Seeger invested $1,700 in 17 acres of land overlooking the Hudson River in Beacon and began building a log cabin there in the late 1940s. In 1949, Mr. Seeger, Mr. Hays, Ronnie Gilbert and Fred Hellerman started working together as the Weavers. They were signed to Decca Records by Gordon Jenkins, the company's music director and an arranger for Frank Sinatra. With Mr. Jenkins's elaborate orchestral arrangements, the group recorded a repertoire that stretched from "If I Had a Hammer" to a South African song, "Wimoweh" (the title was Mr. Seeger's mishearing of "Mbube," the name of a South African hit by Solomon Linda), to an Israeli soldiers' song, "Tzena, Tzena, Tzena," to a cleaned-up version of Lead Belly's "Goodnight, Irene." Onstage, they also sang more pointed topical songs.
In 1950 and 1951 the Weavers were national stars, with hit singles and engagements at major nightclubs. Their hits included "Kisses Sweeter Than Wine" and Mr. Guthrie's "So Long (It's Been Good to Know Yuh)," and they sold an estimated four million singles and albums.
But "Red Channels," an influential pamphlet listing performers with suspected Communist ties, appeared in June 1950 and listed Mr. Seeger, although by then he had quit the Communist Party. He would later criticize himself for having not left the party sooner, though he continued to describe himself as a "communist with a small c.' "
Despite the Weavers' commercial success, by the summer of 1951 the "Red Channels" citation and leaks from F.B.I. files had led to the cancellation of television appearances. In 1951, the Senate Internal Security Subcommittee investigated the Weavers for sedition. And in February 1952, a former member of People's Songs testified before the House Un-American Activities Committee that three of the four Weavers were members of the Communist Party.
As engagements dried up the Weavers disbanded, though they reunited periodically in the mid-1950s. After the group recorded an advertisement for Lucky Strike cigarettes, Mr. Seeger left, citing his objection to promoting tobacco use.
Shut out of national exposure, Mr. Seeger returned primarily to solo concerts, touring college coffeehouses, churches, schools and summer camps, building an audience for folk music among young people. He started to write a long-running column for the folk-song magazine Sing Out! And he recorded prolifically for the independent Folkways label, singing everything from children's songs to Spanish Civil War anthems.
In 1955 he was subpoenaed by the House Un-American Activities Committee, where he testified, "I feel that in my whole life I have never done anything of any conspiratorial nature." He also stated: "I am not going to answer any questions as to my association, my philosophical or religious beliefs or my political beliefs, or how I voted in any election, or any of these private affairs. I think these are very improper questions for any American to be asked, especially under such compulsion as this."
Mr. Seeger offered to sing the songs mentioned by the congressmen who questioned him. The committee declined.
Mr. Seeger was indicted in 1957 on 10 counts of contempt of Congress. He was convicted in 1961 and sentenced to a year in prison, but the next year an appeals court dismissed the indictment as faulty. After the indictment, Mr. Seeger's concerts were often picketed by the John Birch Society and other rightist groups. "All those protests did was sell tickets and get me free publicity," he later said. "The more they protested, the bigger the audiences became."
By then, the folk revival was prospering. In 1959, Mr. Seeger was among the founders of the Newport Folk Festival. The Kingston Trio's version of Mr. Seeger's "Where Have All the Flowers Gone?" reached the Top 40 in 1962, soon followed by Peter, Paul and Mary's version of "If I Had a Hammer," which rose to the Top 10.
Mr. Seeger was signed to a major label, Columbia Records, in 1961, but he remained unwelcome on network television. "Hootenanny," an early-1960s show on ABC that capitalized on the folk revival, refused to book Mr. Seeger, causing other performers (including Bob Dylan, Joan Baez and Peter, Paul and Mary) to boycott it. "Hootenanny" eventually offered to present Mr. Seeger if he would sign a loyalty oath. He refused.
He toured the world, performing and collecting folk songs, in 1963, and returned to serenade civil rights advocates, who had made a rallying song of his "We Shall Overcome."
Like many of Mr. Seeger's songs, "We Shall Overcome" had convoluted traditional roots. It was based on old gospel songs, primarily "I'll Overcome," a hymn that striking tobacco workers had sung on a picket line in South Carolina. A slower version, "We Will Overcome," was collected from one of the workers, Lucille Simmons, by Zilphia Horton, the musical director of the Highlander Folk School in Monteagle, Tenn., which trained union organizers.
Ms. Horton taught it to Mr. Seeger, and her version of "We Will Overcome" was published in the People's Songs newsletter. Mr. Seeger changed "We will" to "We shall" and added verses ("We'll walk hand in hand"). He taught it to the singers Frank Hamilton, who would join the Weavers in 1962, and Guy Carawan, who became musical director at Highlander in the 50s. Mr. Carawan taught the song to the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee at its founding convention.
The song was copyrighted by Mr. Seeger, Mr. Hamilton, Mr. Carawan and Ms. Horton. "At that time we didn't know Lucille Simmons's name," Mr. Seeger wrote in his 1993 autobiography, "Where Have All the Flowers Gone." All of the song's royalties go to the "We Shall Overcome" Fund, administered by what is now the Highlander Research and Education Center, which provides grants to African-Americans organizing in the South.
Along with many elders of the protest-song movement, Mr. Seeger felt betrayed when Bob Dylan appeared at the 1965 Newport Folk Festival with a loud electric blues band. Reports emerged that Mr. Seeger had tried to cut the power cable with an ax, but witnesses including the producer George Wein and the festival's production manager, Joe Boyd (later a leading folk-rock record producer), said he did not go that far. (An ax was available, however. A group of prisoners had used it while singing a logging song.)
As the United States grew divided over the Vietnam War, Mr. Seeger wrote "Waist Deep in the Big Muddy," an antiwar song with the refrain "The big fool says to push on." He performed the song during a taping of "The Smothers Brothers Comedy Hour" in September 1967, his return to network television, but it was cut before the show was broadcast. After the Smothers Brothers publicized the censorship, Mr. Seeger returned to perform the song for broadcast in February 1968.
During the late 1960s Mr. Seeger started an improbable project: a sailing ship that would crusade for cleaner water on the Hudson River. Between other benefit concerts he raised money to build the Clearwater, a 106-foot sloop that was launched in June 1969 with a crew of musicians. The ship became a symbol and a rallying point for antipollution efforts and education.
In May 2009, after decades of litigation and environmental activism led by Mr. Seeger's nonprofit environmental organization, Hudson River Sloop Clearwater, General Electric began dredging sediment containing PCBs it had dumped into the Hudson. Mr. Seeger and his wife also helped organize a yearly summer folk festival named after the Clearwater.
In the 80s and 90s Mr. Seeger toured regularly with Arlo Guthrie, Woody's son, and continued to lead singalongs and perform benefit concerts. Recognition and awards arrived. He was elected to the Songwriters Hall of Fame in 1972, and in 1993 he was given a lifetime achievement Grammy Award. In 1994, President Bill Clinton handed him the National Medal of Arts, America's highest arts honor, given by the National Endowment for the Arts. In 1999, he traveled to Cuba to receive the Order of Félix Varela, Cuba's highest cultural award, for his "humanistic and artistic work in defense of the environment and against racism."
In 1996, Mr. Seeger was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame as an early influence. Arlo Guthrie, who paid tribute at the ceremony, mentioned that the Weavers' hit "Goodnight, Irene" reached No. 1, only to add, "I can't think of a single event in Pete's life that is probably less important to him." Mr. Seeger made no acceptance speech, but he did lead a singalong on "Goodnight, Irene," flanked by Stevie Wonder, David Byrne and members of the Jefferson Airplane.
Mr. Seeger won Grammy Awards for best traditional folk album in 1997, for the album "Pete," and in 2009, for the album "At 89." He also won a Grammy in the children's music category in 2011 for "Tomorrow's Children."
WRITE A orming into the 21st century, despite a flagging voice; audiences happily sang along more loudly. He celebrated his 90th birthday, on May 3, 2009, at a Madison Square Garden concert a benefit for Hudson River Sloop Clearwater with Mr. Springsteen, Dave Matthews, John Mellencamp, Joan Baez, Ani DiFranco, Roger McGuinn of the Byrds, Emmylou Harris and dozens of other musicians paying tribute. In August he was back in Newport for the 50th anniversary of the Newport Folk Festival.Mr. Seeger's wife, Toshi, died in 2013, days before the couple's 70th anniversary. Survivors include his son, Daniel; his daughters, Mika and Tinya; a half-sister, Peggy; and six grandchildren, including the musician Tao Rodriguez-Seeger, who performed with him at the Obama inaugural. His half-brother Mike Seeger, a folklorist and performer who founded the New Lost City Ramblers, died in 2009.
Through the years, Mr. Seeger remained determinedly optimistic. "The key to the future of the world," he said in 1994, "is finding the optimistic stories and letting them be known."
"Let me issue and control a nation's money and I care not who writes the laws. - Mayer Rothschild
"Civil disobedience is not our problem. Our problem is civil obedience! People are obedient in the face of poverty, starvation, stupidity, war, and cruelty. Our problem is that grand thieves are running the country. That's our problem!" - Howard Zinn
"If there is no struggle there is no progress. Power concedes nothing without a demand. It never did and never will" - Frederick Douglass
Posts: 379
Threads: 84
Likes Received: 0 in 0 posts
Likes Given: 0
Joined: Jun 2013
Pete Seeger biographer David King Dunaway writes, "If JFK became the most famous graduate of the [Harvard] Class of '40, Pete Seeger was its best-known dropout." Pete Seeger's uncle Alan Seeger was the poet who died in World War I and wrote John F. Kennedy's favorite poem, "I Have a Rendezvous with Death."
Posts: 17,312
Threads: 3,465
Likes Received: 0 in 0 posts
Likes Given: 2
Joined: Sep 2008
This is very sad news and he will be greatly missed. But I do rejoice in that he lived a long and incredibly fruitful life, saving America's cultural heritage, inspiring millions who loved his songs, nurturing other talents to blossom, and that he had good health and died a natural death in his sleep unlike so many others from this side of fascism.
The networks may have tried to ban him but I see he made it to the Johnny Cash Show
Still playing until the last.
Pete Seeger 'The Power of Song' PBS (2007)
"The philosophers have only interpreted the world, in various ways. The point, however, is to change it." Karl Marx
"He would, wouldn't he?" Mandy Rice-Davies. When asked in court whether she knew that Lord Astor had denied having sex with her.
“I think it would be a good idea” Ghandi, when asked about Western Civilisation.
Posts: 16,285
Threads: 1,789
Likes Received: 7 in 7 posts
Likes Given: 0
Joined: Sep 2008
The entire hour show of DemocracyNow! is devoted to a loving memory of the often guest on DN! - Peter Seeger...do watch. http://www.democracynow.org/2014/1/28/we..._folk_icon
The legendary folk singer and activist Pete Seeger died Monday at the age of 94. For nearly seven decades, Seeger was a musical and political icon who helped create the modern American folk music movement. We air highlights of two appearances by Seeger on Democracy Now!, including one of his last television interviews recorded just four months ago. Interspersed in the interviews, Seeger sings some of his classic songs, "We Shall Overcome," "If I Had A Hammer" and "Where Have All the Flowers Gone." He also talks about what has been described as his "defiant optimism." "Realize that little things lead to bigger things. That's what [the album] Seeds' is all about," Seeger said. "And this wonderful parable in the New Testament: the sower scatters seeds. Some seeds fall in the pathway and get stamped on, and they don't grow. Some fall on the rocks, and they don't grow. But some seeds fall on fallow ground, and they grow and multiply a thousand fold. Who knows where some good little thing that you've done may bring results years later that you never dreamed of."
Seeger led an illustrious musical career. In the 1940s, he performed in the Almanac Singers with Woody Guthrie. Then he formed The Weavers. In the 1950s, he was blacklisted after he opposed Senator Joseph McCarthy's political witch hunt and was almost jailed for refusing to answer questions before the House Un-American Activities Committee. Seeger became a prominent civil rights activist and helped popularize the anthem "We Shall Overcome." In the 1960s, he was a vocal critic of the Vietnam War and inspired a generation of protest singers. He was later at the center of the environmental and anti-nuclear movements. With his wife Toshi, Pete helped found Clearwater, a group to clean up the Hudson River. Toshi died last year just weeks before their 70th wedding anniversary. In 2009, he and Bruce Springsteen performed Guthrie's "This Land is Your Land" on the steps of the Lincoln Memorial at an inaugural concert for Barack Obama.
"Let me issue and control a nation's money and I care not who writes the laws. - Mayer Rothschild
"Civil disobedience is not our problem. Our problem is civil obedience! People are obedient in the face of poverty, starvation, stupidity, war, and cruelty. Our problem is that grand thieves are running the country. That's our problem!" - Howard Zinn
"If there is no struggle there is no progress. Power concedes nothing without a demand. It never did and never will" - Frederick Douglass
Posts: 16,285
Threads: 1,789
Likes Received: 7 in 7 posts
Likes Given: 0
Joined: Sep 2008
[TABLE="width: 100%"]
[TR]
[TD="width: 84%"] Pete Seeger (1919-2014): He Changed the World One Song at a Time
By John Whitehead [/TD]
[TD="width: 16%"][/TD]
[/TR]
[/TABLE]
"My job is to show folks there's a lot of good music in this world, and if used right it may help to save the planet."-- Pete Seeger"The world will be saved by people fighting for their homes. Homes will be saved by people who fight for the world."-- Pete Seeger
Pete Seeger, the 94-year-old activist-singer-songwriter who tried to change the world with every note he uttered, has died, and we are all the poorer for it.
A longtime friend whose letters I treasured for their hand-drawn embellishments and whose words of encouragement urged me to keep on fighting, Seeger belonged to a dying breed of Americans who cared more about making a difference using whatever resources were available to them than luxuriating in creature comforts and basking in the glow of their greatness.
Long before the Beatles or the Rolling Stones, Jim Hendrix or Bob Dylan, there was Pete Seeger, a lone ranger fighting injustice with little more than a five-string banjo in hand and a gift for putting words to music. Unarguably one of the most important musical influences of the 20th century, Seeger helped to lay the foundation for American protest music, singing out about the plight of everyday working folks and urging listeners to political and social activism.
Born in New York City on May 3, 1919, Seeger, whose father was a pacifist musicologist, was plunged into the world of music and politics from an early age. He studied sociology at Harvard University until 1938, when he dropped out and spent the summer bicycling through New England and New York, painting watercolors of farmers' houses in return for food. Looking for but failing to get a job as a newspaper reporter in New York City, he then worked at the Archives of American Folk Music at the Library of Congress in Washington, D.C. In 1940, Seeger met Woody Guthrie at a Grapes of Wrath migrant-worker benefit concert. Seeger, Guthrie, Lee Hays and Millard Lampell joined together to form the Almanac Singers, which became known for its political radicalism and support of communism.
In 1942, Seeger was drafted by the U.S. Army and sent to Saipan in the Western Pacific. After the war, he helped start the People's Songs Bulletin, later Sing Out! magazine, which combined information on folk music with social criticism. In 1950, Seeger formed The Weavers with Lee Hays, Ronnie Gilbert and Fred Hellerman. Targeted for the political messages behind some of their songs, the group was blacklisted and banned from television and radio.
In 1955, the House Committee on Un-American Activities subpoenaed Seeger to appear before them (read his testimony here). During the hearings, Seeger refused to disclose his political views and the names of his political associates. When asked by the committee to name for whom he had sung, Seeger replied:
I am saying voluntarily that I have sung for almost every religious group in the country, from Jewish and Catholic, and Presbyterian and Holy Rollers and Revival Churches, and I do this voluntarily. I have sung for many, many different groups--and it is hard for perhaps one person to believe, I was looking back over the twenty years or so that I have sung around these forty-eight states, that I have sung in so many different places.
He was sentenced to one year in jail but, quoting the First Amendment, successfully appealed the decision after spending four hours behind bars. Nevertheless, he was blacklisted most of his life from normal radio and television work.
During the 1960s, Seeger traveled around the country, continuing to play his folk songs for the peace and civil rights movements. Deeply offended by the U.S. involvement in Vietnam, Seeger, along with other folk singers such as Joan Baez, led many protests.
"Wherever he was asked, when the need was the greatest, he, like Kilroy, was there. And still is," said his long-time friend, Studs Terkel. "Though his voice is somewhat shot, he holds forth on that stage. Whether it be a concert hall, a gathering in the park, a street demonstration, any area is a battleground for human rights."
In 1963, Seeger recorded the now-famous gospel song "We Shall Overcome." In 1965, he sang it on the 50-mile walk from Selma to Montgomery, Alabama, with Martin Luther King, Jr. and 1,000 other marchers. That song would go on to become the anthem for the civil rights movement and be translated into many languages. Seeger also turned his attention to cleaning up the Hudson River that ran past his home. In 1966, he helped form Clearwater, an organization dedicated to educating the public on environmental concerns such as pollution and protecting the river. The group offers educational programs for children on a 76-foot replica of a traditional Hudson cargo sloop and holds a two-day festival on the banks of the Hudson River every June.
Seeger was awarded the Presidential Medal of the Arts and the prestigious Kennedy Center Award in 1994. In 1996, he was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame for his contribution to music and to the development of rock and folk music. In April of that year, he received the Harvard Arts Medal, and after decades of creating songs, in 1997, Seeger won a Grammy Award for Best Traditional Folk Album for his album, Pete. In May 2009, a broad cross-section of musicians including Bruce Springsteen, Dave Matthews, John Mellencamp, Joan Baez, Ani DiFranco, Roger McGuinn of the Byrds, Emmylou Harris and others assembled at Madison Square Garden to pay tribute to Seeger and celebrate his 90th birthday.
Right up until the end, Seeger never stopped speaking out and he never stopped urging young people to follow their hearts and take initiative: "Well, here's hoping all the foregoing will help you avoid a few dead-end streets (we all hit some), and here's hoping enough of your dreams come true to keep you optimistic about the rest. We've got a big world to learn how to tie together. We've all got a lot to learn. And don't let your studies interfere with your education."
In an interview I conducted with Pete Seeger several years ago, I asked him whether he had found an answer to the question "When will they ever learn?" which he repeatedly posed in his song, "Where Have All the Flowers Gone."
Seeger's response is one for the books:
We will never know everything. But I think if we can learn within the next few decades to face the danger we all are in, I believe there will be tens of millions, maybe hundreds of millions, of human beings working wherever they are to do something good. I tell everybody a little parable about the "teaspoon brigades." Imagine a big seesaw. One end of the seesaw is on the ground because it has a big basket half full of rocks in it. The other end of the seesaw is up in the air because it's got a basket one quarter full of sand. Some of us have teaspoons and we are trying to fill it up. Most people are scoffing at us. They say, "People like you have been trying for thousands of years, but it is leaking out of that basket as fast as you are putting it in." Our answer is that we are getting more people with teaspoons every day. And we believe that one of these days or years--who knows--that basket of sand is going to be so full that you are going to see that whole seesaw going zoop! in the other direction. Then people are going to say, "How did it happen so suddenly?" And we answer, "Us and our little teaspoons over thousands of years."
But I don't think we have forever. I now believe that all technological societies tend to self-destruct. The reason is that the very things that make us a successful technological society, such as our curiosity, our ambition and determination, will also cause us to fall.
Rest in peace, Pete, and not to worry. I and the other ragtag members of your teaspoon brigade will keep working to change the world one teaspoon at a time.
The Seeger interview in its entirety is available here.
"Let me issue and control a nation's money and I care not who writes the laws. - Mayer Rothschild
"Civil disobedience is not our problem. Our problem is civil obedience! People are obedient in the face of poverty, starvation, stupidity, war, and cruelty. Our problem is that grand thieves are running the country. That's our problem!" - Howard Zinn
"If there is no struggle there is no progress. Power concedes nothing without a demand. It never did and never will" - Frederick Douglass
Posts: 16,285
Threads: 1,789
Likes Received: 7 in 7 posts
Likes Given: 0
Joined: Sep 2008
The Salem News
ALBANY, N.Y. (AP) Unable to carry his beloved banjo, Pete Seeger used a different but equally formidable instrument, his mere presence, to instruct yet another generation of young people how to effect change through song and determination two years ago.
A surging crowd, two canes and seven decades as a history-sifting singer and rabble-rouser buoyed him as he led an Occupy Wall Street protest through Manhattan in 2011.
"Be wary of great leaders," he told The Associated Press two days after the march. "Hope that there are many, many small leaders."
The banjo-picking troubadour who sang for migrant workers, college students and star-struck presidents in a career that introduced generations of Americans to their folk music heritage died Monday at age 94. Seeger's grandson, Kitama Cahill-Jackson, said his grandfather died peacefully in his sleep around 9:30 p.m. at New York-Presbyterian Hospital, where he had been for six days. Family members were with him.
"He was chopping wood 10 days ago," Cahill-Jackson recalled.
With his lanky frame, use-worn banjo and full white beard, Seeger was an iconic figure in folk music who outlived his peers. He performed with the great minstrel Woody Guthrie in his younger days and wrote or co-wrote "If I Had a Hammer," "Turn, Turn, Turn," "Where Have All the Flowers Gone" and "Kisses Sweeter Than Wine." He lent his voice against Hitler and nuclear power. A cheerful warrior, he typically delivered his broadsides with an affable air and his fingers poised over the strings of his banjo.
In the early '60s, Seeger docked his sailboat Clearwater in Marblehead Harbor, and he performed at an outdoor concert in Crocker Park at the Marblehead Arts Festival.
In 2011, he walked nearly 2 miles with hundreds of protesters swirling around him holding signs and guitars, later admitting the attention embarrassed him. But with a simple gesture extending his friendship Seeger gave the protesters and even their opponents a moment of brotherhood the short-lived Occupy movement sorely needed.
When a policeman approached, Tao Rodriguez-Seeger said at the time he feared his grandfather would be hassled.
"He reached out and shook my hand and said, Thank you, thank you, this is beautiful,'" Rodriguez-Seeger said. "That really did it for me. The cops recognized what we were about. They wanted to help our march. They actually wanted to protect our march because they saw something beautiful. It's very hard to be anti-something beautiful."
That was a message Seeger spread his entire life.
With The Weavers, a quartet organized in 1948, Seeger helped set the stage for a national folk revival. The group Seeger, Lee Hays, Ronnie Gilbert and Fred Hellerman churned out hit recordings of "Goodnight Irene," "Tzena, Tzena" and "On Top of Old Smokey."
Seeger also was credited with popularizing "We Shall Overcome," which he printed in his publication "People's Song" in 1948. He later said his only contribution to the anthem of the civil rights movement was changing the second word from "will" to "shall," which he said "opens up the mouth better."
"Every kid who ever sat around a campfire singing an old song is indebted in some way to Pete Seeger," Arlo Guthrie once said.
His musical career was always braided tightly with his political activism, in which he advocated for causes ranging from civil rights to the cleanup of his beloved Hudson River. Seeger said he left the Communist Party around 1950 and later renounced it. But the association dogged him for years.
He was kept off commercial television for more than a decade after tangling with the House Un-American Activities Committee in 1955. Repeatedly pressed by the committee to reveal whether he had sung for Communists, Seeger responded sharply: "I love my country very dearly, and I greatly resent this implication that some of the places that I have sung and some of the people that I have known, and some of my opinions, whether they are religious or philosophical, or I might be a vegetarian, make me any less of an American."
He was charged with contempt of Congress, but the sentence was overturned on appeal.
Seeger called the 1950s, years when he was denied broadcast exposure, the high point of his career. He was on the road touring college campuses, spreading the music he, Guthrie, Huddie "Lead Belly" Ledbetter and others had created or preserved.
"The most important job I did was go from college to college to college to college, one after the other, usually small ones," he told The Associated Press in 2006. " ... And I showed the kids there's a lot of great music in this country they never played on the radio."
His scheduled return to commercial network television on the highly rated Smothers Brothers variety show in 1967 was hailed as a nail in the coffin of the blacklist. But CBS cut out his Vietnam protest song, "Waist Deep in the Big Muddy," and Seeger accused the network of censorship.
He finally got to sing it five months later in a stirring return appearance, although one station, in Detroit, cut the song's last stanza: "Now every time I read the papers/That old feelin' comes on/We're waist deep in the Big Muddy/And the big fool says to push on."
Seeger's output included dozens of albums and single records for adults and children.
He appeared in the movies "To Hear My Banjo Play" in 1946 and "Tell Me That You Love Me, Junie Moon" in 1970. A reunion concert of the original Weavers in 1980 was filmed as a documentary titled "Wasn't That a Time."
By the 1990s, no longer a party member but still styling himself a communist with a small C, Seeger was heaped with national honors.
Official Washington sang along the audience must sing was the rule at a Seeger concert when it lionized him at the Kennedy Center in 1994. President Bill Clinton hailed him as "an inconvenient artist who dared to sing things as he saw them."
President Barack Obama on Tuesday said Seeger used his voice to strike blows for worker's and civil rights, world peace, and environmental conservation.
Seeger was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 1996 as an early influence. Ten years later, Bruce Springsteen honored him with "We Shall Overcome: The Seeger Sessions," a rollicking reinterpretation of songs sung by Seeger. While pleased with the album, Seeger said he wished it was "more serious." A 2009 concert at Madison Square Garden to mark Seeger's 90th birthday featured Springsteen, Dave Matthews, Eddie Vedder and Emmylou Harris among the performers.
Seeger was a 2014 Grammy Awards nominee in the Best Spoken Word category, which Stephen Colbert won.
Seeger's sometimes ambivalent relationship with rock was most famously on display when Dylan "went electric" at the 1965 Newport Folk Festival.
Witnesses say Seeger became furious backstage as the amped-up band played, though just how furious is debated. Seeger dismissed the legendary tale that he looked for an ax to cut Dylan's sound cable, and said his objection was not to the type of music but only that the guitar mix was so loud you couldn't hear Dylan's words.
Seeger maintained his reedy 6-foot-2 frame into old age, though he wore a hearing aid and conceded that his voice was pretty much shot. He relied on his audiences to make up for his diminished voice, feeding his listeners the lines and letting them sing out.
"I can't sing much," he said. "I used to sing high and low. Now I have a growl somewhere in between."
Nonetheless, in 1997 he won a Grammy for best traditional folk album, "Pete."
Seeger was born in New York City on May 3, 1919, into an artistic family whose roots traced to religious dissenters of colonial America. His mother, Constance, played violin and taught; his father, Charles, a musicologist, was a consultant to the Resettlement Administration, which gave artists work during the Depression. His uncle Alan Seeger, the poet, wrote "I Have a Rendezvous With Death."
Pete Seeger said he fell in love with folk music when he was 16, at a music festival in North Carolina in 1935. His half brother, Mike Seeger, and half sister, Peggy Seeger, also became noted performers.
He learned the five-string banjo, an instrument he rescued from obscurity and played the rest of his life in a long-necked version of his own design. On the skin of Seeger's banjo was the phrase, "This machine surrounds hate and forces it to surrender" a nod to his old pal Guthrie, who emblazoned his guitar with "This machine kills fascists."
Dropping out of Harvard in 1938 after two years as a disillusioned sociology major, he hit the road, picking up folk tunes as he hitchhiked or hopped freights.
"The sociology professor said, Don't think that you can change the world. The only thing you can do is study it,'" Seeger said in October 2011.
In 1940, with Guthrie and others, he was part of the Almanac Singers and performed benefits for disaster relief and other causes.
He and Guthrie also toured migrant camps and union halls. He sang on overseas radio broadcasts for the Office of War Information early in World War II. In the Army, he spent 3½ years in Special Services, entertaining soldiers in the South Pacific, and made corporal.
He married Toshi Seeger on July 20, 1943. The couple built their cabin in Beacon after World War II and stayed on the high spot of land by the Hudson River for the rest of their lives together. The couple raised three children. Toshi Seeger died in July at age 91.
The Hudson River was a particular concern of Seeger's. He took the sloop Clearwater, built by volunteers in 1969, up and down the Hudson, singing to raise money to clean the water and fight polluters.
He also offered his voice in opposition to racism and the death penalty. He got himself jailed for five days for blocking traffic in Albany in 1988 in support of Tawana Brawley, a black teenager whose claim of having been raped by white men was later discredited. He continued to take part in peace protests during the war in Iraq, and he continued to lend his name to causes.
"Can't prove a damn thing, but I look upon myself as old grandpa," Seeger told the AP in 2008 when asked to reflect on his legacy. "There's not dozens of people now doing what I try to do, not hundreds, but literally thousands. ... The idea of using music to try to get the world together is now all over the place."
"Let me issue and control a nation's money and I care not who writes the laws. - Mayer Rothschild
"Civil disobedience is not our problem. Our problem is civil obedience! People are obedient in the face of poverty, starvation, stupidity, war, and cruelty. Our problem is that grand thieves are running the country. That's our problem!" - Howard Zinn
"If there is no struggle there is no progress. Power concedes nothing without a demand. It never did and never will" - Frederick Douglass
|
![[Image: 28seeger1-master675.jpg]](http://static01.nyt.com/images/2014/01/28/arts/music/28seeger1/28seeger1-master675.jpg) Launch media viewer
Launch media viewer