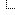04-03-2015, 02:19 PM
http://time.com/3730128/heroin-deaths-painkillers/
Heroin-Related Deaths Have Quadrupled in America
New federal data reports bad news for America's heroin problem Heroin-related deaths quadrupled in the U.S. within just three years, according to new federal data. The new report from the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) shows that from 2010 to 2013, drug-poisoning deaths involving heroin increased fourfold, from 0.7 deaths per 100,000 people to 2.7 deaths per 100,000 people. The rate was about four times higher among men than among women in 2013.
Heroin-related drug-poisoning deaths have increased in all age groups, races and ethnic groups, the data show. Every region in the U.S. also experienced an increase, and the Midwest experienced the biggest jump. One reason for the spike is America's growing painkiller problem. The NCHS released another report last month showing that significantly more people over age 20 are using opioids. The number of people who used a painkiller stronger than morphine increased from 17% to 37% from the early 2000s to about a decade later.
![[Image: attachment.php?attachmentid=6774&stc=1]](https://deeppoliticsforum.com/forums/attachment.php?attachmentid=6774&stc=1)
People who are hooked on painkillers may make the switch to heroin since it's cheaper and doesn't need a prescription, according to Dr. Andrew Kolodny, the chief medical officer of the Phoenix House, a national nonprofit drug and alcohol-rehabilitation organization. Both drugs come from the opium poppy and therefore offer a similar high. "We are seeing heroin deaths sky rocketing because we have an epidemic of people addicted to opioids. There are new markets like suburbs where heroin didn't used to exist," says Kolodny. (He was not involved in the research.)
Prior data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show that painkillers are a growing problem. In 2014, the CDC reported that physicians wrote 259 million painkiller prescription in a single year the equivalent of a bottle of pills per American and almost 50 Americans die every day from a prescription-painkiller overdose. The agency recommends that states run prescription-drug prescribing databases to track overprescribing and consider policies that reduce risky prescribing practices.
As states and the White House struggle to tackle opioid addiction, some experts are skeptical about whether such efforts are enough to solve the problem. "We are dealing with the worst drug epidemic in our history," says Kolodny. "There's no evidence it's plateauing."
Heroin-Related Deaths Have Quadrupled in America
New federal data reports bad news for America's heroin problem Heroin-related deaths quadrupled in the U.S. within just three years, according to new federal data. The new report from the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) shows that from 2010 to 2013, drug-poisoning deaths involving heroin increased fourfold, from 0.7 deaths per 100,000 people to 2.7 deaths per 100,000 people. The rate was about four times higher among men than among women in 2013.
Heroin-related drug-poisoning deaths have increased in all age groups, races and ethnic groups, the data show. Every region in the U.S. also experienced an increase, and the Midwest experienced the biggest jump. One reason for the spike is America's growing painkiller problem. The NCHS released another report last month showing that significantly more people over age 20 are using opioids. The number of people who used a painkiller stronger than morphine increased from 17% to 37% from the early 2000s to about a decade later.
People who are hooked on painkillers may make the switch to heroin since it's cheaper and doesn't need a prescription, according to Dr. Andrew Kolodny, the chief medical officer of the Phoenix House, a national nonprofit drug and alcohol-rehabilitation organization. Both drugs come from the opium poppy and therefore offer a similar high. "We are seeing heroin deaths sky rocketing because we have an epidemic of people addicted to opioids. There are new markets like suburbs where heroin didn't used to exist," says Kolodny. (He was not involved in the research.)
Prior data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show that painkillers are a growing problem. In 2014, the CDC reported that physicians wrote 259 million painkiller prescription in a single year the equivalent of a bottle of pills per American and almost 50 Americans die every day from a prescription-painkiller overdose. The agency recommends that states run prescription-drug prescribing databases to track overprescribing and consider policies that reduce risky prescribing practices.
As states and the White House struggle to tackle opioid addiction, some experts are skeptical about whether such efforts are enough to solve the problem. "We are dealing with the worst drug epidemic in our history," says Kolodny. "There's no evidence it's plateauing."
"All that is necessary for tyranny to succeed is for good men to do nothing." (unknown)
James Tracy: "There is sometimes an undue amount of paranoia among some conspiracy researchers that can contribute to flawed observations and analysis."
Gary Cornwell (Dept. Chief Counsel HSCA): "A fact merely marks the point at which we have agreed to let investigation cease."
Alan Ford: "Just because you believe it, that doesn't make it so."
James Tracy: "There is sometimes an undue amount of paranoia among some conspiracy researchers that can contribute to flawed observations and analysis."
Gary Cornwell (Dept. Chief Counsel HSCA): "A fact merely marks the point at which we have agreed to let investigation cease."
Alan Ford: "Just because you believe it, that doesn't make it so."